Planning external radiotherapy for womb cancer
The radiotherapy team plan your external radiotherapy before you start treatment. This means working out the dose of radiotherapy you need and exactly where you need it.
Your planning appointment takes from 15 minutes to 2 hours.
The planning CT scan
You usually have a planning CT scan in the radiotherapy department.
The scan shows the cancer and the area around it. You might have other types of scans or x-rays to help your treatment team plan your radiotherapy. The plan they create is just for you.
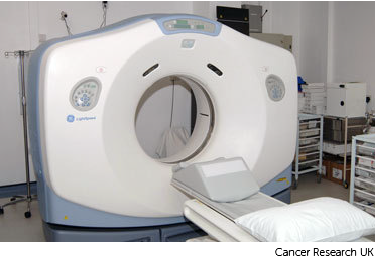
Your radiographers tell you what is going to happen. They help you into position on the scan couch. You might have a type of firm cushion called a vacbag to help you keep still.
The CT scanner couch is the same type of bed that you lie on for your treatment sessions. You need to lie very still. Tell your radiographers if you aren't comfortable.
Before the scan
Before your scan, you might need to drink a few cups of water. You will also need to drink before your treatment sessions. This is so that you have a full bladder, which is roughly the same size and in the same position every day.
You may also need to have an empty bowel. Your doctor will prescribe medication to ensure you open your bowels regularly. They may also ask you to give yourself an enema. This will empty your back passage before the planning scan and treatments.
Your radiographer or doctor might put a little marker inside the top of your vagina. The marker is usually a little piece of metal. This shows the position of the vagina clearly on the scan. The marker is taken out after the scan has finished.
Injection of dye
You might need an injection of contrast into a vein in your hand. This is a dye that helps body tissues show up more clearly on the scan.
Before you have the contrast, your radiographer asks you about any medical conditions or allergies. Some people are allergic to the contrast.
Having the scan
Once you are in position, your radiographers put some markers on your skin. They move the couch up and through the scanner. They then leave the room, and the scan starts.
The scan takes about 5 minutes. You won't feel anything. Your radiographers can see and hear you from the CT control area where they operate the scanner.
Ink and tattoo marks
The radiographers make pin point sized tattoo marks on your skin. They use these marks to line you up into the same position every day. The tattoos make sure they treat exactly the same area for all of your treatments. They may also draw marks around the tattoos with a permanent ink pen, so that they are clear to see when the lights are low.
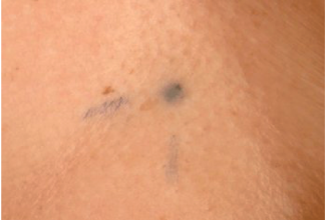
The radiotherapy staff tell you how to look after the markings. The pen marks might start to rub off in time, but the tattoos won’t. Tell your radiographer if that happens. Don't try to redraw them yourself.
After your planning session
You might have to wait a few days or up to 3 weeks before you start treatment.
During this time the physicists and your radiotherapy doctor (clinical oncologist) decide the final details of your radiotherapy plan. They make sure that the area of the cancer will receive a high dose and nearby areas receive a low dose. This reduces the side effects you might get during and after treatment.



