Creating your radiotherapy plan
For your planning scan, you lie on the scanner couch in the same position that you will have your radiotherapy treatment.
While you are lying on the scanning couch, the radiographer takes several measurements. They might make pen marks and very small permanent ink marks (tattoos) on your skin in the treatment area. This is to make sure they can get you in the right position each time you have your treatment.
The information from the scan and measurements are put into the planning computer. Your radiotherapy team then work out the best position for the radiotherapy beams. The computer software helps plan how to give a high dose of radiation to the cancer, while avoiding as much healthy tissue as possible.
Reading CT or MRI scans
This picture shows a typical CT scan cross section (slice). The slice shown is of the bottom of the rib cage. Note that the left on this scan is actually the right side of the body.
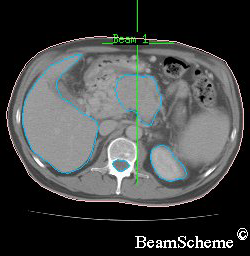
This is what you can see:
- on the left is a large crescent – this is the liver
- on the right, at the bottom, is a round shape – this is the kidney
- in the centre, at the bottom, is a lighter round shape – this is the spinal cord inside the backbone
- in the middle is an irregular shape, which is the pancreas with a cancer inside it
Looking at the tumour in 3D
A radiotherapy planning computer can create a 3D picture of the cancer from CT scans and sometimes other types of scan. This picture shows a 3D computer image.
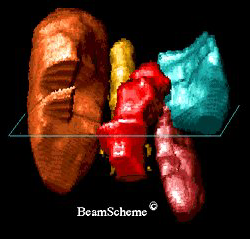
This is what you can see:
- the cancer is shown in red
- the liver is shown in brown
- the spleen is shown in blue/green
- the left kidney is shown in pink
- the spine is shown in yellow
Looking at a 3D picture can be very useful when planning treatment. It can be rotated and looked at from different angles. This helps your radiotherapy doctor (clinical oncologist) work out the best way to arrange the radiotherapy beams to cover the whole cancer and miss the major organs.
Building the radiotherapy plan
To treat cancer, one or more radiation beams are pointed at the cancer. The area where all the beams meet is where the cancer is (or where it used to be before surgery). This is where you have the highest dose of radiotherapy.
This picture shows how 3 radiation beams can be directed at the cancer. The white lines show the middle of the beams. The beams are actually like torch beams so they get wider as they travel away from the radiotherapy machine. By the time they reach the cancer each beam may be up to 8 to 10 cm in width.
This picture is of the bottom of the rib cage.
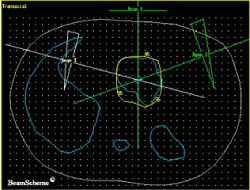
- on the left is a large crescent – this is the liver
- on the right, at the bottom, is a round shape – this is the kidney
- in the centre, at the bottom, is a smaller round shape – this is the spinal cord inside the backbone
- in the middle is an irregular shape – this is the pancreas with a cancer inside it
One beam is aimed from in front of the patient. This is the beam at the top of the picture.
The other two beams are aimed from the sides at an angle so that they avoid the spinal cord and kidney.
Marking your skin
Once the treatment area is lined up, the radiographers make some marks on your skin.
Your radiographers use these marks to set up the radiotherapy machine in the same way every day.



