Types of melanoma
Melanoma starts in cells called melanocytes. You have melanocytes in your skin. Other places you have them include:
- the layer of tissue lining some parts of your body (mucous membrane)
- your eyes
Melanoma skin cancer
Melanoma that starts in the skin is called melanoma skin cancer or cutaneous melanoma.
There are different types of melanoma skin cancer. The different types are usually treated in the same way.
These pictures are examples of different types of melanoma skin cancer. If you're worried about any moles or skin changes, it's important to see your GP to get them checked.
The pictures on this page have been provided by the St John's Institute of Dermatology at Guy's and St Thomas' Hospital.
Superficial spreading melanoma
Superficial spreading melanoma tends to start growing across the skin before growing deeper down into it.
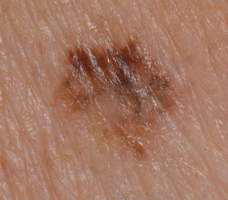
It's the most common type of melanoma. 70 to 80 out of every 100 people with melanoma (70% to 80%) have this type.
It can develop anywhere on the body. But in men it's most common on the central part of the body (the trunk). And in women, it's most common on the legs.
Nodular melanoma
Nodular melanomas tend to grow downwards into the deeper layers of skin. They can grow quite quickly. There is often a raised area on the skin surface with this type of melanoma.
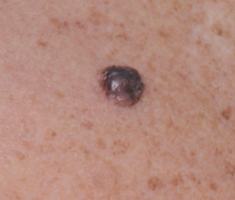
It's the second most common type of melanoma. Between 9 and 15 out of every 100 melanomas (between 9% and 15%) are nodular melanomas. It's most often diagnosed in people in their 40’s and 50's. It can develop on any part of the body.
Lentigo maligna melanoma
These melanomas develop from very slow growing coloured patches of skin. Doctors call these patches lentigo maligna or Hutchinson's melanotic freckle.
A lentigo maligna is flat and grows outwards in the surface layers of the skin. It might slowly get bigger over several years and might change shape or colour. If it becomes a lentigo maligna melanoma, it starts to grow down into the deeper layers of the skin. It may also form lumps called nodules.
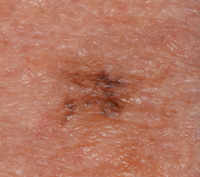
Between 5 and 15 out of every 100 melanomas (between 5% and 15%) are this type. It's most common in people older than 60 years. They appear in areas of skin that get a lot of sun exposure, so are most common on the head and neck. They are also more common in people who have spent a lot of time in the sun.
Rare types of melanoma skin cancer
Acral lentiginous melanoma
Acral lentiginous melanoma is usually found on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. It can also grow under or around the nails. It's much more common on the feet than on the hands.
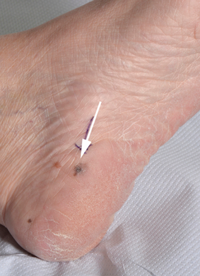
This type of melanoma is rare. Only 1 to 3 out of every 100 people diagnosed with melanoma (1% to 3%) have acral lentiginous melanoma. But it's the most common type of melanoma in people with brown or black skin. It's also most often diagnosed in middle aged and older adults.
Desmoplastic melanoma
Desmoplastic melanoma can develop anywhere on your body but it’s most common in the head and neck area.
It's often the same colour as your skin and can look like a scar. This type of melanoma is more common in men than women.
Other rare melanoma skin cancers
These include:
- spitzoid melanoma
- malignant blue neavus
Amelanotic melanoma
Rarely melanoma skin cancers can be red or skin coloured rather than dark (pigmented). These are called amelanotic melanomas which means without melanin. Melanin is a dark coloured pigment.
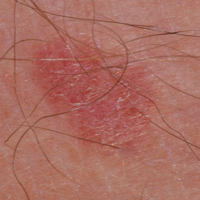
Any type of melanoma can be amelanotic. This can make them difficult to diagnose as they may be mistaken for other skin conditions.
Mucosal melanoma
Melanoma that starts in the mucous membrane is called mucosal melanoma.
Although it is rare, it can develop in the:
anus 
vagina 
- penis
vulva 
- mouth
digestive system 
These areas are all lined by the mucous membrane which makes  .
.
Treatments for mucosal melanoma depends on which part of the body the melanoma is in, and the chance of it coming back. Treatments include:
- surgery
- radiotherapy
- targeted or immunotherapy drugs
- chemotherapy
The targeted cancer drugs, immunotherapy and chemotherapy used to treat mucosal melanoma may be different to those used to treat melanoma skin cancer.
If you know what drug treatments you're going to have, you can read more about them in our cancer drugs A to Z.
Melanoma of the eye
Rarely, melanoma can start in the eye.
The most common type of melanoma of the eye starts in the uvea. The uvea is the middle layer of the eye and has 3 parts. These are the:
- iris (the coloured part of the eye)
- ciliary body
- choroid
Melanomas that start in the uvea are called uveal melanomas. Most of these develop in the choroid part of the uvea. So, your doctor might call it a choroid melanoma.
Melanomas of the eye are treated in a different way to melanoma skin cancer.



